Create, edit, and collaborate with others on documents from your Android phone or tablet with the free Google Docs app. With Google Docs you can: – Create new documents or edit any that were created on the web or on another device. – Share documents and work together with others in the same document at the same time.
The Settings app on Android includes a screen called Developer options that letsyou configure system behaviors that helpyou profile and debug your app performance. For example, you can enable debugging over USB, capturea bug report, enable visual feedback for taps,flash window surfaces when they update, use the GPU for 2D graphics rendering, and more.
Note:- On Android 4.1 and lower, the Developer options screen is available by default. On Android 4.2 and higher, you must enable this screen. To enable developer options, tap the Build Number option 7 times.
- If you need a rollback of Google Docs, check out the app's version history on Uptodown. It includes all the file versions available to download off Uptodown for that app. Download rollbacks of Google Docs for Android. Any version of Google Docs distributed on Uptodown is completely virus-free and free to download at no cost.
- Android 4.2 on the Nexus 4. Android 4.2 Jelly Bean is a version of Android. Similar to version 4.1, it has the name Jelly Bean. Version 4.2.0 had many glitches, and gained a lot of the lag that version 4.1 had removed. Not long after the devices had the 4.2.0 update, they received the 4.2.1 update.
- Each account must go through the Google Android setup process and once complete, each can apply its own settings and secure login. Android 4.2 supports up to eight total accounts including the owner, and each has its own apps and media, but “any user can accept updated app permissions on behalf of all users,” according to an Android prompt.
Enable developer options and USB debugging
On Android 4.1 and lower, the Developer options screen is available by default. On Android 4.2 and higher, you must enable this screen. To enable developer options, tap the Build Number option 7 times. You can find this option in one of the following locations, depending on your Android version:
- Android 9 (API level 28) and higher: Settings > About Phone > Build Number
- Android 8.0.0 (API level 26) and Android 8.1.0 (API level 26): Settings > System > About Phone > Build Number
- Android 7.1 (API level 25) and lower: Settings > About Phone > Build Number
At the top of the Developer options screen, you can toggle the options on and off(figure 1). You probably want to keep this on.When off, most options are disabled except those that don't require communication between thedevice and your development computer.
Before you can use the debugger and other tools, you need to enable USB debugging, which allows Android Studio and other SDK tools to recognize your device when connected via USB. To enable USB debugging, toggle the USB debugging option in the Developer Options menu. You can find this option in one of the following locations, depending on your Android version:
- Android 9 (API level 28) and higher: Settings > System > Advanced > Developer Options > USB debugging
- Android 8.0.0 (API level 26) and Android 8.1.0 (API level 26): Settings > System > Developer Options > USB debugging
- Android 7.1 (API level 25) and lower: Settings > Developer Options > USB debugging
The rest of this page describes some of the other options available on this screen.
General options
On Android 8.0 and higher, you can tap Quick settings developer tiles to add selected developer options to your Quick Settings panel. After you select one or more of the available tiles (figure 2), open the Quick Settings panel and tap the pencil to enter edit mode. Then, drag the developer tiles from the tiles pane onto the Quick settings panel, and tap the pencil again to exit edit mode.
Figure 2. Add to Quick Settings panel
Other general options include the following:
- Memory: (On Android 8.0 and higher) Display memory stats, such as average memory usage, memory performance, total memory available, average memory used, how much free memory is available, and how much memory is being used by apps.
- Take bug report: Get a copy of the current device log files to share with someone. When you get a notification that the bug report is ready, tap the notification to share it.
- System UI demo mode: Makes it easier to take clean screenshots by displaying a generic, preset notification bar that does not show notifications or low battery warnings. Enable Demo Mode allows you to change the appearance of the status bar usingadb demo mode commands. Or you can use Show Demo Mode to hide notifications and display a preset status bar.Note:The adb demo mode commands might not work on all devices because they are not verifiedduring Android certification testing. They're only verified to work on Nexus and Pixel devices.
- Desktop backup password: Sets a backup password so you can use adb commands to back up and restore device apps and data under password protection.
- Stay awake: Sets your screen to stay on every time you plug it in.
- Enable Bluetooth Host Controller Interface (HCI) snoop log: Captures all Bluetooth HCI packets in a file stored at
/sdcard/btsnoop_hci.log. You can retrieve the packets, and then use a program like Wireshark to analyze and troubleshoot the information.
Debugging
Debugging options provide ways to configure on-device debugging, and to establish communication between the device and your development computer.
Enable USB debugging (figure 3) so your Android device can communicate with your development machine through Android Debug Bridge (adb). The Wait for Debugger option is unavailable until you use Select debug app to select the app to debug. If you enable Wait for Debugger, the selected app waits for the debugger to attach before it executes.
Other debugging options include the following:
- Store logger data persistently on device: Select the type of log messages you want to store persistently on the device. Options are off, all, all but radio, or kernel only.
- Select mock location app: Use this option to fake the GPS location of the device to test whether your app behaves the same in other locations. To use this option, download and install a GPS mock location app.
- Enable view attribute inspection: Saves view attribute information in the
mAttributesmember variable of aViewinstance so it can be used for debugging. You can access the attribute information through the Layout Inspector user interface, as shown in Figure 4 (without this enabled, the 'Attributes' item is not available). - Enable GPU debug layers: Available on devices running Android 9 (API level 28) and higher, enable this option to allow loading Vulkan validation layers from local device storage. To learn more, read Vulkan validation layers on Android.
Figure 4. View attributes
Networking
Networking options provide ways to configure Wi-Fi and DHCP settings.
Tap Select USB Configuration to specify how you want the computer to identify the device. As shown in figure 5, you can configure devices for charging only, to transfer files (MTP), to transfer pictures (PTP), to use your mobile internet on the PC (RNDIS), or to transfer audio or MIDI files.
Tap Bluetooth AVRCP version and select the profle version you want to use to control all of the Bluetooth A/V equipment to which your device has access. Addiitonally, to fine-tune the audio playback on the device, tap and set the following options:
- Bluetooth Audio Codec: Adjust the sound quality (codec) of your devices by selecting one of the following codecs:
- SBC: Transfer data to Bluetooth audio output devices such as headphones and speakers.
- AAC: Better sound quality from wired devices than MP3 at similar bit rates.
- aptX: A pure wireless sound in high-quality smartphones, speakers, soundbars, headphones, and tablets.
- aptX HD: High-resolution streaming to Bluetooth devices.
- LDAC: Provide high-quality music listening over wireless connections.
- Enable Optional Codecs and Disable Optional Codecs: If you have additional codec implementations installed, use these options to enable and disable them.
- Bluetooth Audio Sample Range: Adjust the number of audio samples per second by selecting an audio codec sample rate. Higher sample rates use more resources.
- Bluetooth Audio Bits Per sample: Set the number of bits of information in each audio sample. With a higher the bit rate, the sound is better but the sample file is larger.
- Bluetooth Audio Channel Mode: Select mono or stereo.
- Bluetooth Audio LDAC Codec: Optimize the sound to increase audio quality, balance audio and connection quality, increase connection quality, or use an adaptive bit rate to balance audio and connection quality.
The followng list describes other ways to configure Wi-Fi and DHCP setup:
- Wireless display certification: Enables advanced configuration controls and settings for Wireless Display certification to the specifications set forth in the Wi-Fi Alliance Wi-Fi Display Specification. The certification applies to Android 4.4 (API level 19) and higher.
- Enable Wi-Fi verbose logging: Increases the Wi-Fi logging level for each wireless network (SSID) you connect to according to its relative received signal strength (RSSI). For more information about logs, see Write and view logs with Logcat.
- Aggressive Wi-Fi to cellular handover: When the signal is low, makes Wi-Fi more efficient in handing over the data connection to a cellular network.
Input
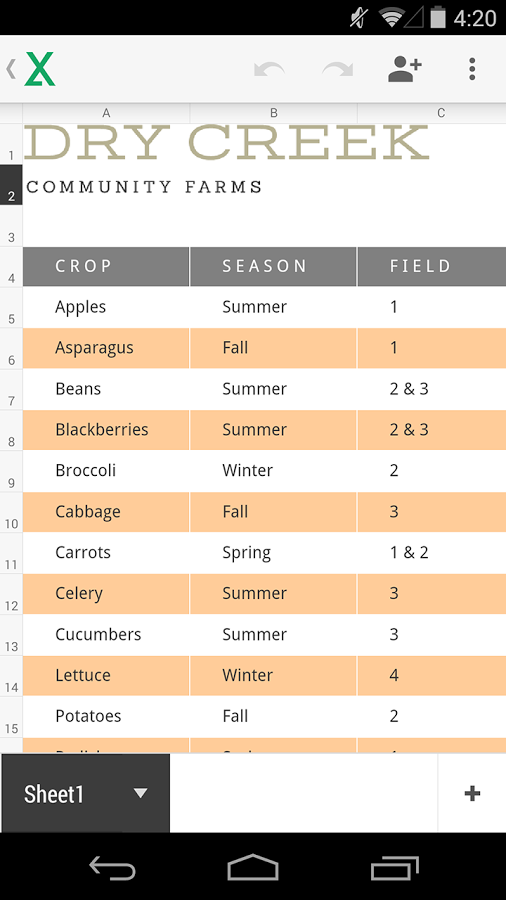
Figure 6. Pointer location
Enable Show taps to display taps when you touch the screen. A circle appears under your finger or stylus and follows you as you move around the screen. A tap works like a pointer when you Record a video on your device.
Google Docs For Android 4.2 2.1
Enable Pointer Location to show the pointer (tap) location on the device with cross-hairs. A bar appears across the top of the screen to track the cross-hair coordinates (figure 6). As you move the pointer, the coordinates in the bar track the cross-hair location and the pointer path draws on the screen.
Drawing
Drawing options provide visual cues about the app's user interface and how it operates.
Enable Show Layout Bounds to show your app's clip bounds, margins, and other user interface constructions on the device, as shown in figure 7.
Other Drawing options include the following:
- Force RTL layout direction: Forces screen layout direction to be from right to left (RTL) or from left to right (default).
- Window animation scale: Sets the window animation playback speed so you can check its performance at different speeds. A lower scale results in a faster speed.
- Transition animation scale: Sets the transition animation playback speed so you can check its performance at different speeds. A lower scale results in a faster speed.
- Simulate secondary displays: Creates a secondary display as an overlay on the device. This is useful when supporting additional displays with the
PresentationAPI. See Secondary displays.
Hardware accelerated rendering
Figure 8. Deuteranomaly color space
Hardware accelerated rendering options provide ways to optimize your app for its target hardware platforms by leveraging hardware-based options such as the GPU, hardware layers, and multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA).
Tap Simulate color space to change the color scheme of the entire device UI. The options refer to types of color blindness. Choices are Disabled (no simulated color scheme), Monochromacy (black, white, and gray), Deuteranomaly (red-green), Protanomaly (red-green), and Tritanomaly (blue-yellow). Protanomaly refers to red-green color blindness with weakness in red colors, and Deuteranomaly (shown in figure 8) refers to red-green color blindness with weakness in green colors.
If you take screenshots in a simulated color space, they appear normal as if you hadn’t changed the color scheme.
Some other ways to leverage hardware-based options are the following:
- Set GPU renderer: Change the default Open GL graphics engine to the Open GL Skia graphics engine.
- Force GPU rendering: Forces apps to use the GPU for 2D drawing, if they were written without GPU rendering by default.
- Show GPU view updates: Displays any onscreen element drawn with the GPU.
- Debug GPU overdraw: Displays color-coding on your device so you can visualize how how many times the same pixel has been drawn in the same frame. The visualization shows where your app might be doing more rendering than necessary. For more information, see Visualize GPU overdraw.
- Debug non-rectangular clip operations: Turns off the clipping area on the canvas to create unusual (non-rectangular) canvas areas. Normally, the clipping area prevents drawing anything outside the bounds of the circular clipping area.
- Force 4x MSAA: Enables multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA) in Open GL ES 2.0 apps.
- Disable HW overlays: Using the hardware overlay enables each app that displays something on the screen to use less processing power. Without the overlay, an app shares the video memory and has to constantly check for collision and clipping to render a proper image. The checking uses a lot of processing power.
Media
Set Disable USB audio routing on to disable automatic routing to external audio devices connected to a computer through a USB port. Automatic routing can interfere with apps that are USB-aware.
In Android 11 and later, when an application without RECORD_AUDIO permission uses UsbManager to request direct access to a USB audio device with audio capture capability (such as a USB headset), a warning message appears asking the user to confirm permission to use the device. The system ignores any 'always use' option, so the user must acknowledge the warning and grant permission every time an app requests access. To avoid this behavior, your app should request the RECORD_AUDIO permission.
Monitoring
Monitoring options provide visual information about app performance, such as long thread and GPU operations.
Tap Profile GPU Rendering and then On screen as bars to display the GPU rendering profile as bars (figure 9). For more information, see Profile GPU rendering.
Apps
App options help you understand how your app operates on the target device.
Tap Background process limit to set the number of processes that can run in the background at one time. Possible settings are shown in figure 10.
Tap Reset ShortcutManager rate-limiting during testing so background apps can continue to call shortcut APIs until the rate limit is reached again. For more information about shortcuts and rate limits, see ShortcutManager.
Enable Don't keep activities to increase battery life by destroying every activity as soon as the user leaves the activity's main view.
The YouTube Android Player API enables you to incorporate video playback functionality into your Android applications. The API defines methods for loading and playing YouTube videos (and playlists) and for customizing and controlling the video playback experience.
Using the API, you can load or cue videos into a player view embedded in your application's UI. You can then control playback programmatically. For example, you can play, pause, or seek to a specific point in the currently loaded video.
You can also register event listeners to get callbacks for certain events, such as the player loading a video or the player state changing. Finally, the API has helper functionality to support orientation changes as well as transitions to fullscreen playback.
How it works
The API client library interacts with a service that is distributed as a part of the YouTube app for the Android platform. The client library has a light footprint, meaning it won't adversely impact your app's file size, if you use ProGuard as part of your build process.
As the API develops, you will be able to access newly introduced API features by upgrading to a newer version of the API client library. However, upgrading is not necessary if you do not care about new features or bug fixes.
In addition, the YouTube app is delivered through the Google Play Store, which means that updates to the API service are not dependent on carrier or OEM system image updates. Generally, devices running Android 2.2 (Froyo) or later that have the Google Play Store app installed will receive updates within a few days. As a result, your application can use the YouTube Android Player API and reach most devices in the Android ecosystem.
Google Docs Android
Note: Users need to run version 4.2.16 of the mobile YouTube app (or higher) to use the API.
Getting Started
The following documents will help you to set up your development environment and use the YouTube Android Player API:
Google Docs For Android 4.2 2018
The download page provides a link to download the API client library and JavaDocs.
The instructions for registering your application explain how to register your app in the Google API Console and to obtain an Android API key, which you will need to use the API.
The setup instructions explain how to set up an API project using either Eclipse or IntelliJ.
The sample applications overview describes the sample applications included in the API download.
The JavaDoc reference provides detailed definitions of the API's interfaces, classes, methods, and enums.
